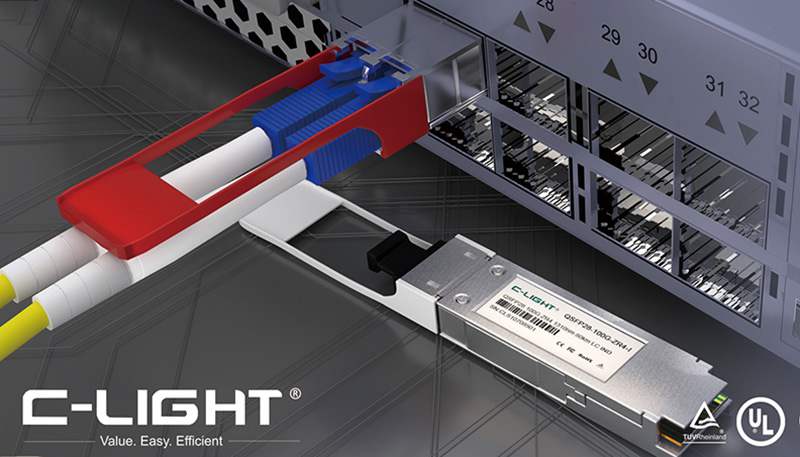
What is the CWDM transceiver? The CWDM transceiver is an optical transceiver that uses CWDM technology to implement the connection between the existing network device and the CWDM mux/demux. When used with a CWDM mux/demux, CWDM transceiver can increase network capacity by transmitting multiple data channels with separate optical wavelengths (1270 nm to 1610 nm) on the same single fiber.
What is the difference between a CWDM transceiver and normal dual-fiber transceiver? A common optical transceiver belongs to a photoelectric conversion device and belongs to an active optical module. Each module has one receiving and two transmitting ports, and the inside of the transmitting port is a laser.The CWDM optical module is a passive module that does not emit laser light itself. Generally, a light plane waveguide (PLC) technology is used to divide a beam of light into several beams of light.
What are the CWDM transceiver package types?
CWDM SFP+ transceiver
The CWDM SFP+ transceiver combines optical signals of different wavelengths and transmits them through one optical fiber through an external wavelength division multiplexer, saving optical fiber resources. At the same time, the receiving end needs to decompose the complex optical signal using a wave decomposition multiplexer. It is divided into 18 bands, from 1270nm to 1610nm, separated by 20nm between each two bands.
CWDM XFP transceiver
The CWDM XFP transceiver is larger than the CWDM SFP+ transceiver. The CWDM XFP optical module complies with the SFP MSA protocol, while the CWDM SFP+ optical module complies with the IEEE802.3ae and SFF-8431, SFF-8432 protocol.
CWDM SFP transceiver
The CWDM SFP transceiver is an optical module that combines CWDM technology. Similar to a traditional SFP, It is a hot-swappable input/output device that plugs into SFP port of a router and connects to the fiber network through this port.
It is an economical and efficient network connectivity solution for networking applications such as Gigabit Ethernet and Fibre Channel (FC) in campus, data center, and metropolitan area networks.
CWDM GBIC transceiver
The GBIC is a hot-swappable input/output device that plugs into a Gigabit Ethernet port or slot to complete a network connection. GBIC is also a transceiver standard, usually used in conjunction with Gigabit Ethernet and Fibre Channel, and is mainly used in Gigabit Ethernet machines and routers. A simple upgrade from the standard LH section, using DFB lasers with specific wavelengths, has facilitated the development of CWDM GBIC modules and DWDM GBIC modules. GBIC transceivers are commonly used for Gigabit Ethernet fiber optic transmission but are also involved in some cases, such as fiber-optic network deceleration, speed-up, and multi-rate transmission applications around 2.5 Gbps.
What are the applications of CWDM transceivers? CWDM transceivers are widely used in CATV (cable TV), FTTH (Fiber to the Home), 1G and 2G Fibre Channel, 100M and Gigabit Ethernet, Synchronous Optical Network SONET OC-3 (155Mbps), OC-12 (622Mbps) And O***8 (2.488Gbps), security and protection systems and other fields.
 TEL:+86 158 1857 3751
TEL:+86 158 1857 3751 



























































 >
>
 >
>
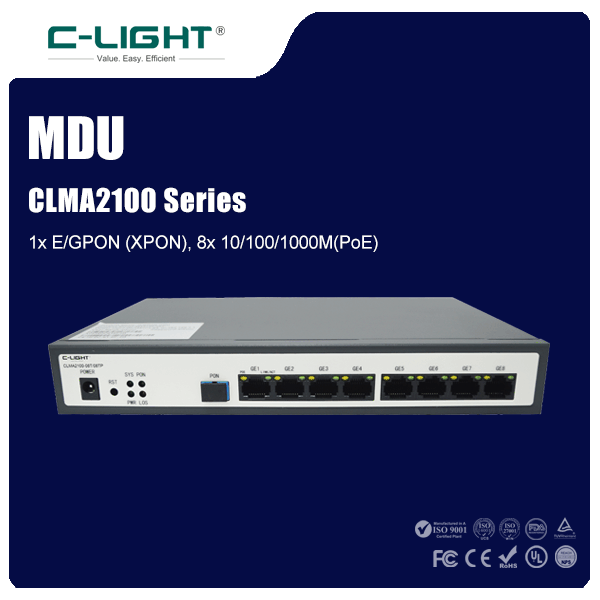 >
>
 >
>
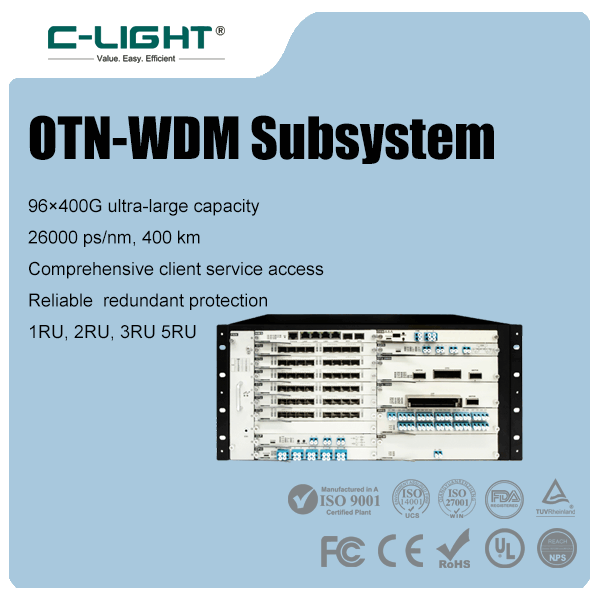 >
>
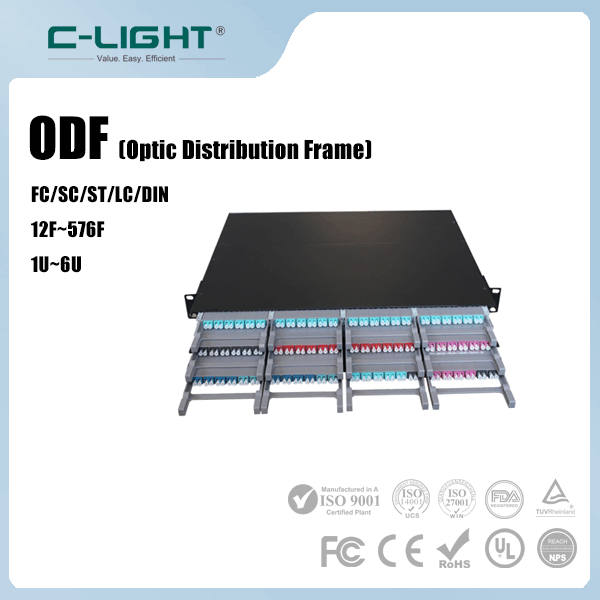 >
>
